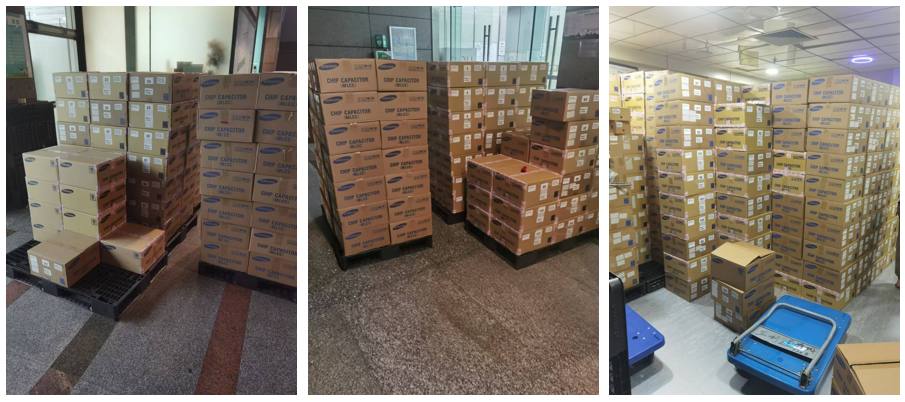
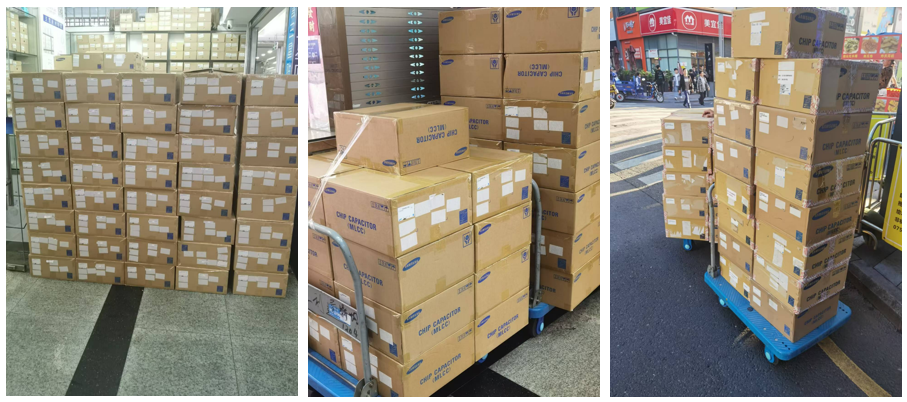
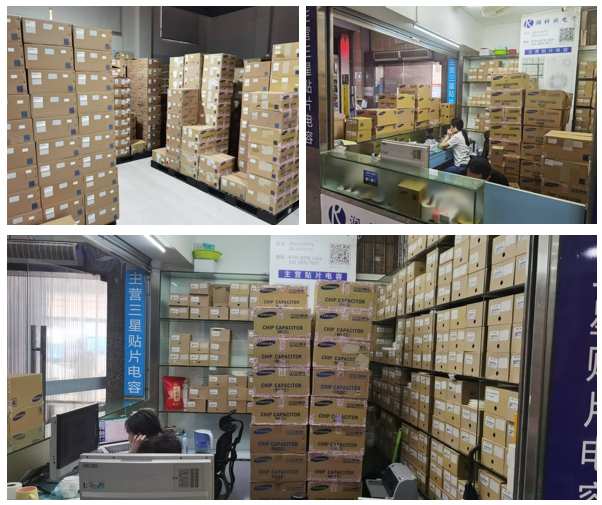



Quantity
Price
Total price
1
$3.2865
$3.2865
10
$2.5200
$25.2000
50
$2.2785
$113.9250
200
$1.9635
$392.7000
600
$1.5330
$919.8000
1000
$1.4280
$1,428.0000
2600
$1.3755
$3,576.3000
5000
$1.3545
$6,772.5000
| TYPE | DESCRIPTION |
| Mfr | CDA (Zhifengwei Technology) |
| Series | CXHP-2.7V |
| Package | Box |
| Product Status | ACTIVE |
| Tolerance | -20%, +80% |
| Package / Case | Radial, Can |
| Size / Dimension | 0.315" Dia (8.00mm) |
| Mounting Type | Through Hole |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C ~ 85°C |
| Lead Spacing | 0.138" (3.50mm) |
| Termination | PC Pins |
| ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance) | 130mOhm @ 1kHz |
| Height - Seated (Max) | 0.709" (18.00mm) |
| Capacitance | 3 F |
| Voltage - Rated | 2.7 V |














